Topographic Maps and Mapping
Topographical maps are useful because they show the terrain and lay of the land as well as feature like roads, structuresand mines. As you read this, it would be helpful if you also had your own topographical map to refer to.
Title
The first thing to notice on a topographical map is the title. It is found in the top right hand corner of the map:
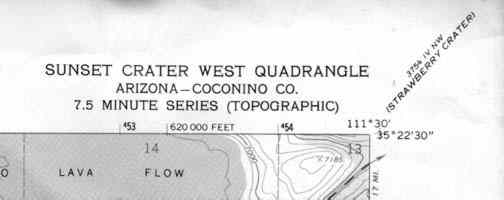
At the corner, but in smaller print is another title. That is the title of the next topographical map to the northeast of this one. You willfind similar titles on all the corners of a topographical map as well as halfwaybetween the corners. Use that information to find the other maps that you may need.
Latitude, Longitude, and UTM'S
The next thing that you should notice on a topographical map are the numbers running all around theoutside of the map. These numbers represent two grid systems that can be used to find your exact location.The first is called latitude and longitude. The exact latitude and longitude is given at each corner ofthat map and at equally spaced intervals between the corners. The second is called UTM's. These are thesmaller bold numbers that run along the border of the map.
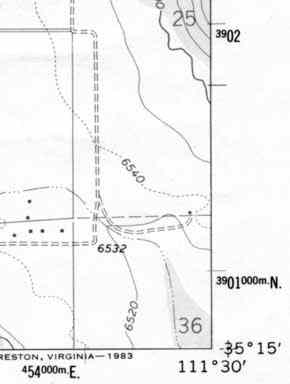
How Accurate Can Latitude and Longitude Get?
At the equator, one degree of latitude or longitude represents approximately 70 statute miles. At higher latitudes the distance of one degree of longitudedecreases. Latitude stays the same because they are always equally spacesapart. If you look on a globe you will see this to be the case. On the otherhand , if you look on a globe you will notice that the lines of longitude getcloser together as they approach the north and south poles.
Degrees are not accurate enough to find a precise location. At best, onedegree of latitude and longitude would define a 70 square mile area. To overcome this problem, 1 degree is divided into 60'(minutes). So if 1 degree equals 70 miles and one degree can be divided into 60' then 1' equals 1.2 miles. Dividing 1 degree into 60' allows one to calculate their position with much better accuracy. In some instances even more accuracy is needed. Todo this we can divide 1' into 60"(seconds). If 1' equals 1.2 miles and we can divide it into 60", then 1" equals 0.02 miles. It it is worth taking a few secondsto memorize the following numbers. It will help you to use latitude andlongitude more effectively:
1 degree = 70 miles 1' = 1.2 miles 1" = .02 miles
UTM Coordinates
UTM Stands for Universal Transverse Mercator. It is another grid system that can be used to find your position. It is most commonly used in the military and for research as well as survey purposes. The UTM system divides thesurface of the earth up into a grid. Each grid is identified by a number across the top called the zone number and a letter down the right hand side called the zone designator. For example, Phoenix Arizona is in UTM grid 12 S.

Every spot within a zone can be defined by a coordinate system that usesmeters. Your vertical position is defined in terms of meters north and yourhorizontal position is given as meters east. They are sometimes referred toas your northing and easting.
Map Scale
Map scale represents the relationship between distance on the map and thecorresponding distance on the ground. The scale on the topo map is found atthe bottom center of the map.
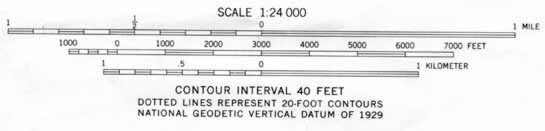
Scale is represented in two different ways on a topographical map. The first isa ratio scale. For ex 1:24,000. What it means is that oneinch on the map represents 24,00 inches on the ground. Below the ratio scaleis a graphic scale representing distance in miles, feet and meters. Thegraphic scale can be used to make fast estimates of distances on the map.The space between the 0 and the 1 mile mark on the scale is the distance youmust go on the map to travel one mile.
Contour Lines
One of the advantages to using a topographical map is that it shows the threedimensional lay of the land. It does this by using contour lines. A contour lineis a line that connects points of equal elevation. On the topo map they appearas the brown lines.
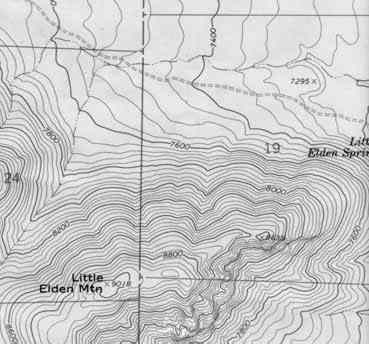
The contour line traces the outline of the terrain at evenly spaced elevations.These are determined by the contour interval. The contour interval is foundbelow the map scale. For this map, the contour interval is 20 feet. That meansthat every time you go up to another brown line the elevation increases by 20feet and every time you go down a brown line the elevation decreases by 20 feet. In the lower left hand corner of the map there is a mountain. Notice howthe contour lines define the shape of the mountain. The lines are closertogether at the top of the mountain where it is steeper. The spacing betweenthe lines decreases as the slope of the mountain decreases.
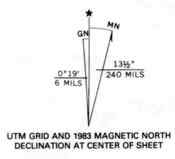
Magnetic Declination
At the lower left hand corner of topographical maps there is a symbol called the magnetic declination. The symbol is used in conjunction with a compass for navigational purposes. The center line with the star above represents the direction of true geographic north. The line coming of to the right represents the direction of magnetic north, When using a compass, the needle always points to magnetic north. The symbol tells you that for the area the map covers, themagnetic compass needle will always point 13.5 degrees to the east of truegeographic north. To the left of the true north line is the grid north line. Thistells you how much the UTM grid and zone lines are offset from true north.
Township & Range
The Township and Range system, sometimes called the Public Lands SurveySystem, was developed to help parcel out western lands as the countryexpanded. The system takes many western states and divides them up usinga base line and a principal meridian:
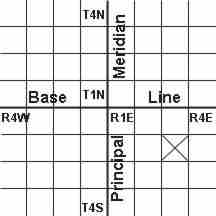
As you go to the east or west of the principal meridian, the range increases inthat direction. If you go north or south of the base line, the townshipincreases. This system divides the land up into townships and ranges thatare 36 square miles each. In the diagram above, the square with the X in itwould be defined as township 2 south (T.2S), range 3 east (R.3E). Eachtownship and range is then subdivided into 36 sections. Each section is onemile square. Individual sections are then subdivided into half sections andquarter sections and so on. On a topo map, you will notice a grid with redlines and text crisscrossing the map. The lines represent the boarders of th







